Datastore Permissions
Purpose and Scope
Datastore permissions are essential for controlling access to your entire Datastore. By configuring these permissions, you establish a primary defense mechanism against unauthorized access and alterations to critical mission data.
Risk of Unrestricted Access
Without proper setup, your application is vulnerable to unregulated access. In such scenarios, every user gains unrestricted access to all datastore resources, posing significant risks.
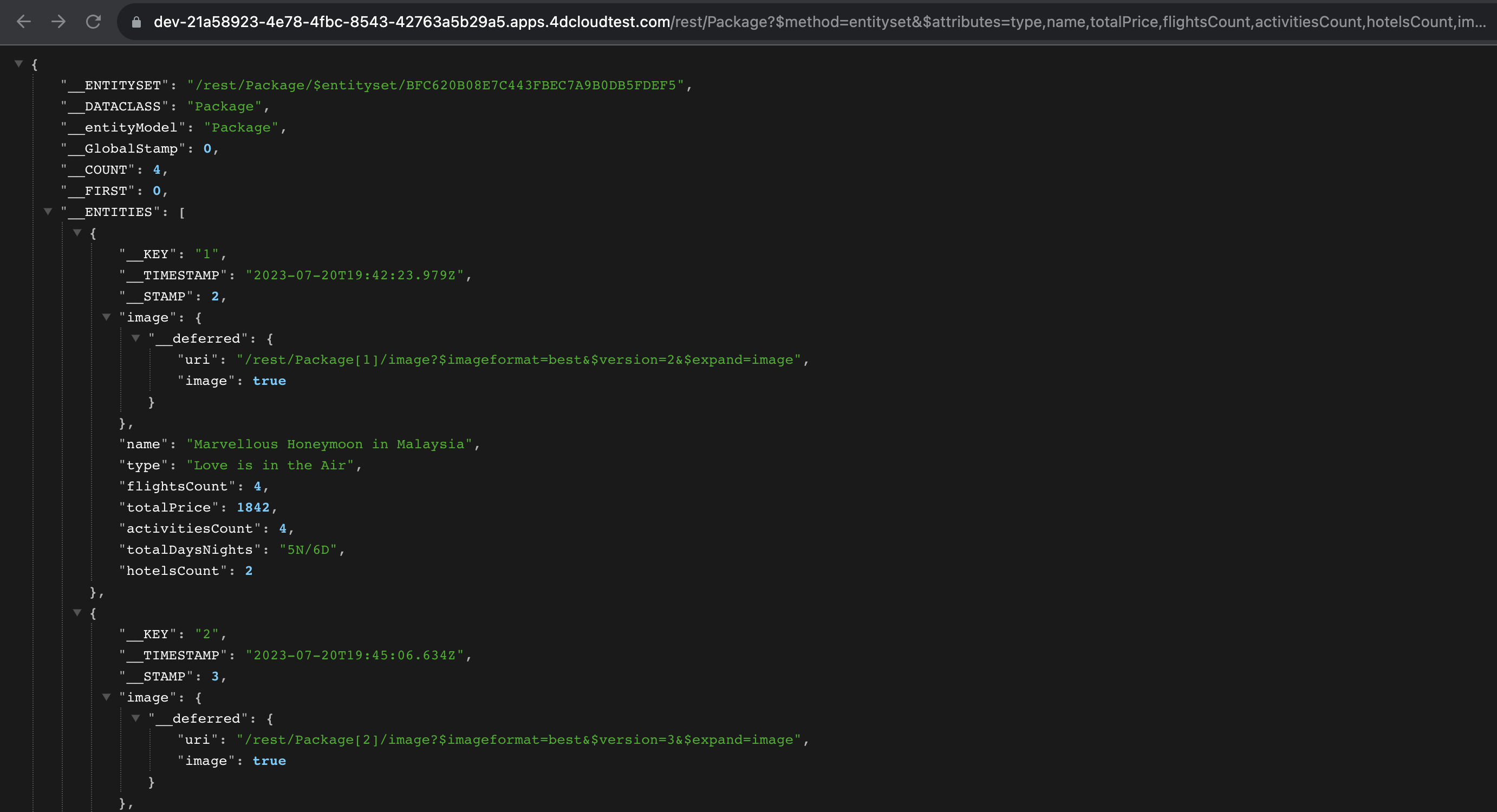
To illustrate, imagine an unauthorized user attempting an HTTP request to the Package dataclass REST API endpoint. This unchecked data access allows unauthorized actions, including accessing confidential user information, and poses a uniform risk across all dataclasses.
Configuring Datastore Permissions
To set permissions for the datastore:
- Select the resource name
ds, from the dropdown list to signify the Datastore resource. - Or, type the resource name
ds, directly into the search bar.
The icon in the dropdown list indicates the Datastore ressource.
Max Restriction to Gradual Expansion
To address the risks of unrestricted access, an approach called All Data Inaccessible by Default is employed. This strategy restricts access to the entire datastore by default, gradually expanding access to specific dataclasses through other privileges achieved by applying Dataclasses Permissions.
Introducing Restricted Privilege
At the core of the datastore lockdown strategy lies the concept of the Restricted privilege. This privilege acts as a safeguard, restricting all actions on the datastore and rendering it inaccessible until specific permissions are meticulously set up.
This ensures that users, even without defined roles or privileges, cannot access any resources within the datastore.
Configuring Permissions
After establishing a privilege like Restricted, you assign permissions to the datastore, covering a range of actions from Read to Execute.
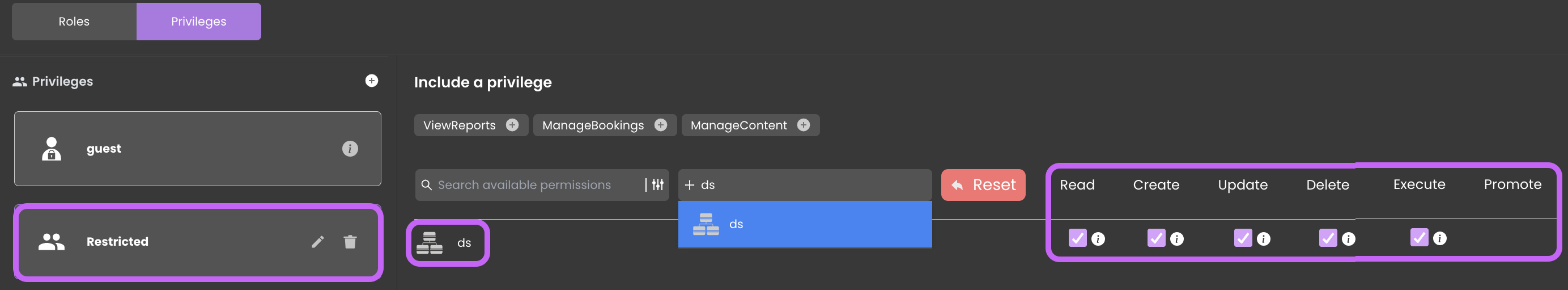
By applying all permissions to the ds resource within the Restricted privilege and not assigning it to any role, you prevent malicious access attempts. This safeguard transforms the application into a secure vault.
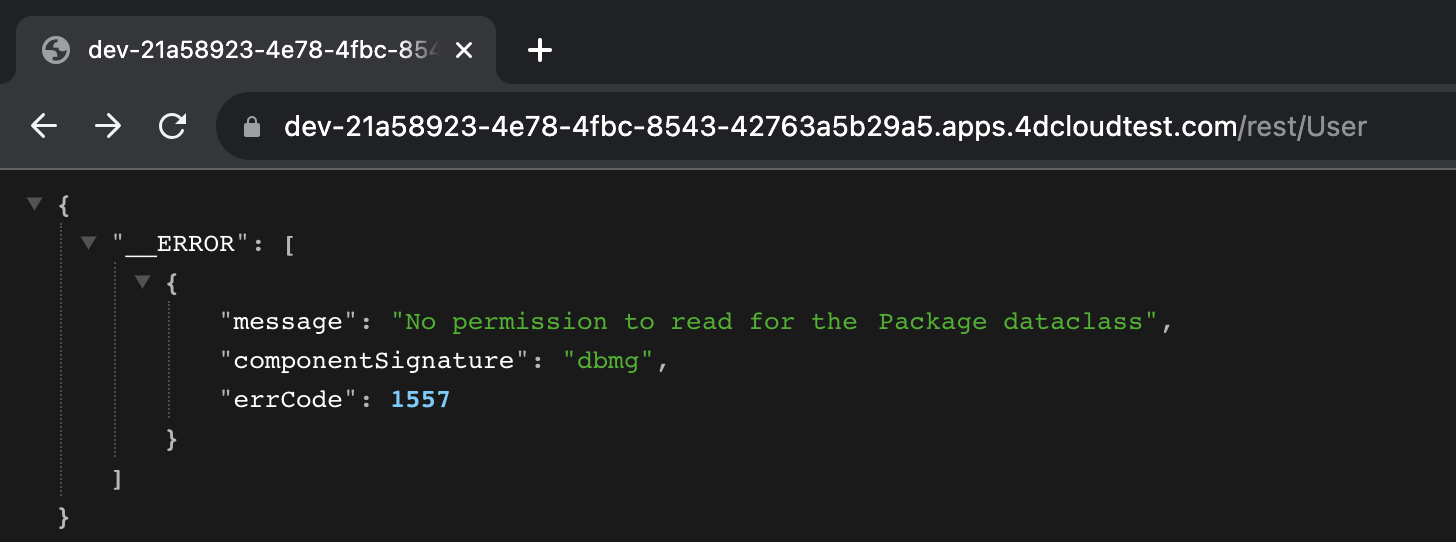
Attempting to access the REST API endpoints will result in a No permission to read for the Package dataclass response, a rule that extends across all dataclasses.
Full Access to Gradual Restriction
Alternatively, the Guest privilege provides another strategy for managing unauthorized users. This privilege allows full access to the entire datastore by default, with specific resources being restricted through other privileges achieved by applying Dataclasses Permissions.
Introducing the Guest Privilege
When a role lacks specific privileges, the Guest privilege is assigned to that Session. This allows users without defined privileges to access non-restricted resources while preventing potentially harmful activities with other resources, ensuring that users interact within well-defined boundaries.
The Guest privilege grants access to all resources if no explicit permissions are in place.
Configuring the Guest Privilege
The Guest privilege is established in the Privileges tab by default, ready to welcome users who have not yet established a formal identity.

Configuring Read Access
To grant read access to the Guest privilege, follow these steps:
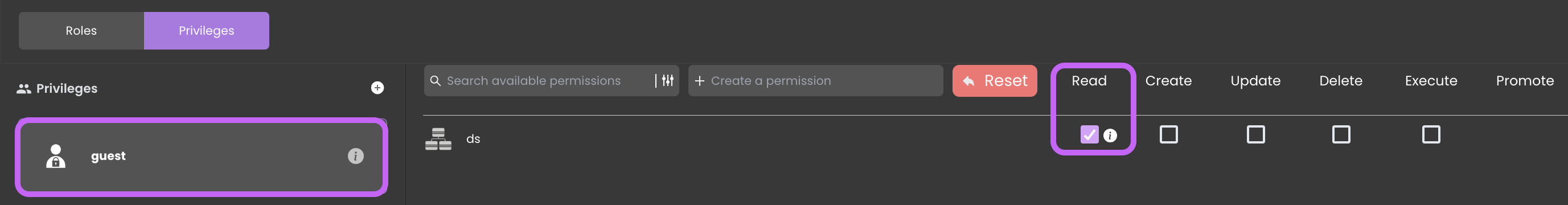
- Remove complete permissions control over the Datastore from the
Restrictedprivilege. - Assign the Read permission specifically to the datastore within the
Guestprivilege, thereby endowing it with the capability of read-only access.
By making this change, the Guest privilege now allows users to access a wealth of data, including details about flights, hotels, and activities, while ensuring that critical information remains safeguarded against unauthorized modifications.
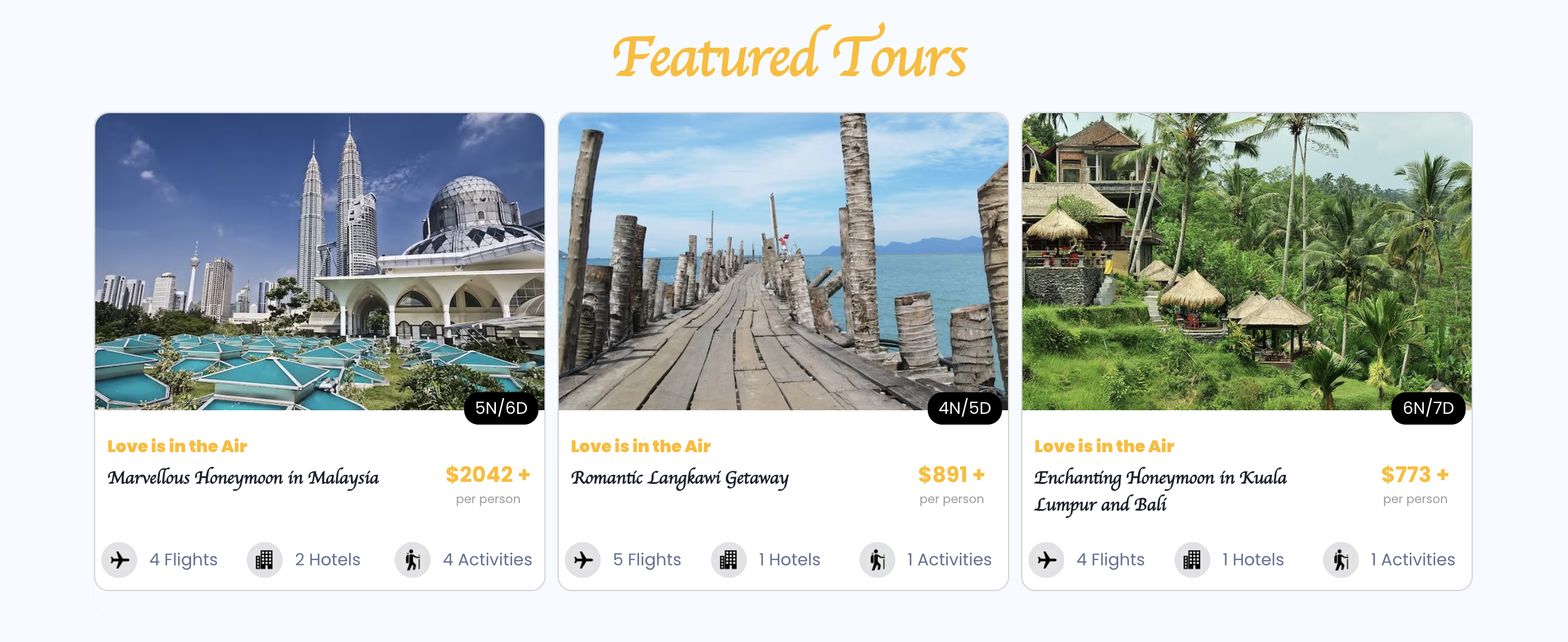
Not all data should be accessible to users. Sensitive user data, confidential reports, and other private information must remain restricted.
To balance data accessibility and security, the next crucial step is to utilize DataClass Permissions to selectively control access to specific sets of data.
Guest Inherited Permission
Permissions of the Guest privilege are automatically inherited across various privileges. This parallels the behavior observed in the Restricted privilege, where the capability of reading from the Datastore is evident.
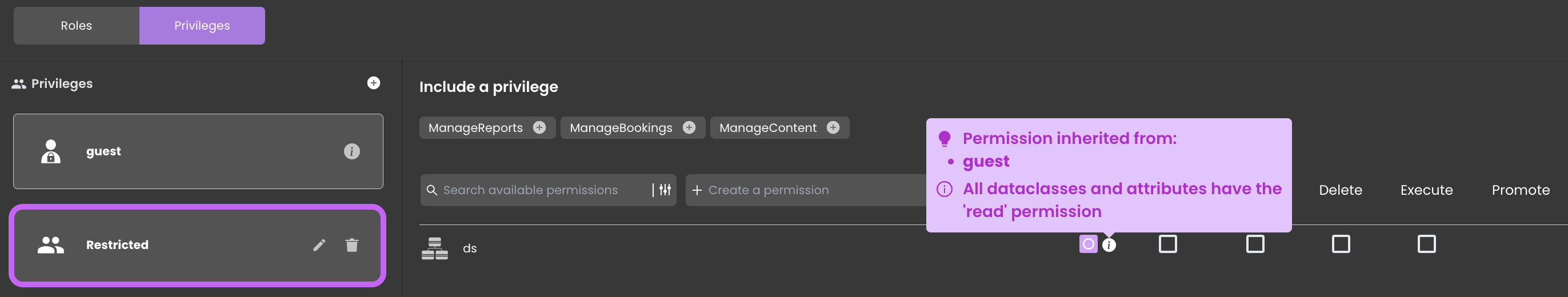
The icon indicates that the permission is inherited, granting access to the resource. However, when you remove this privilege, the inherited permissions also vanish from the privilege that was receiving them.
You can retain the inherited permission by checking the checkbox , ensuring that even if the originating privilege is deleted, the permission set on the resource remains intact.