Function Permissions
Purpose and Scope
Function-level permissions control access to custom functions defined within the Model. These functions can perform actions such as managing bookings, generating invoices, and handling reservations.
Configuring Function Permissions
To configure Function Permissions for a specific privilege, follow these steps:
- Choose the resource name, like the
registerfunction, from the dropdown list. - Alternatively, type the resource name, such as the
registerfunction, directly into the search bar.
- The
icon in the dropdown list indicates Function ressources.
- The
icon in the dropdown list indicates Singleton function ressources.
If the Singleton class or its exposed functions don't appear in the permissions dropdown, follow these steps to enable it:
-
Navigate to the Singleton class in the class section.
-
Check if the Singleton class is missing any exposed functions.
-
If there are no exposed functions, add at least one. Here’s an example:
.
-
Save the changes and re-check the permissions dropdown.
-
If the Singleton class and its exposed functions still don't appear, reload the changes by following the documentation for applying the latest updates.
Now, the Singleton class and its exposed functions should be available for selection, whether it’s the standard class Singleton or the shared one.
Execute Permission
Execute permissions allow the designated privilege to run the function's code .
If the Execute function permission checkbox has the icon on the right, it signifies that the function has been promoted by another privilege. Hover over the privilege name, and clicking on it will redirect you to the privilege promoting the function.

Promote Permission
Promote permissions enable temporary privilege escalation during function execution , ensuring the secure performance of critical operations within that function's code without permanently adding privileges.
Upon executing a specific function within a session with a designated privilege, Qodly dynamically integrates the privileges that Promote the function into the session. This temporary elevation allows the function's execution, even when the original session's privilege lacks direct permission for resources in that function code.
After the function concludes, the temporary elevation from the Promote permission is revoked.
A function can be promoted from multiple privileges. In such cases, there's no hierarchy determining priority.
Instead, the session experiencing temporary privilege elevation during function execution, will have access to all resource permissions set in each of the promoting privileges.

Refer to the use case of the Promote permission for detailed configuration information.
Strategies
Max Restriction to Gradual Expansion
To control function execution, the DataStore level is configured exclusively for the Restricted privilege, ensuring that only roles with this privilege can execute functions, thus preventing any unauthorized access.
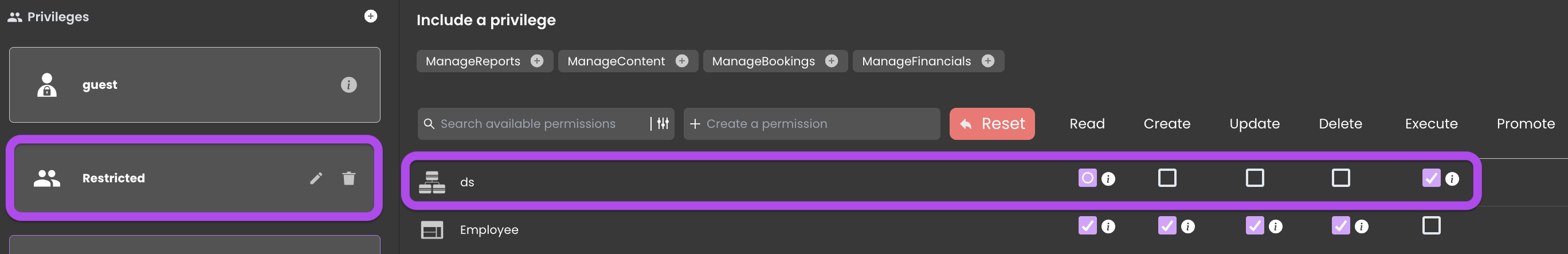
Hovering over the icon reveals that all functions throughout the model — encompassing DataStore, Dataclasses, Entity selections, and Entities — have the execute permission for the Restricted privilege.

However, to accommodate scenarios where the Agent role needs to execute functions, such as the book function within the roomOptions Entity class, a gradual expansion involves adding the book function resource and checking the execute permission.
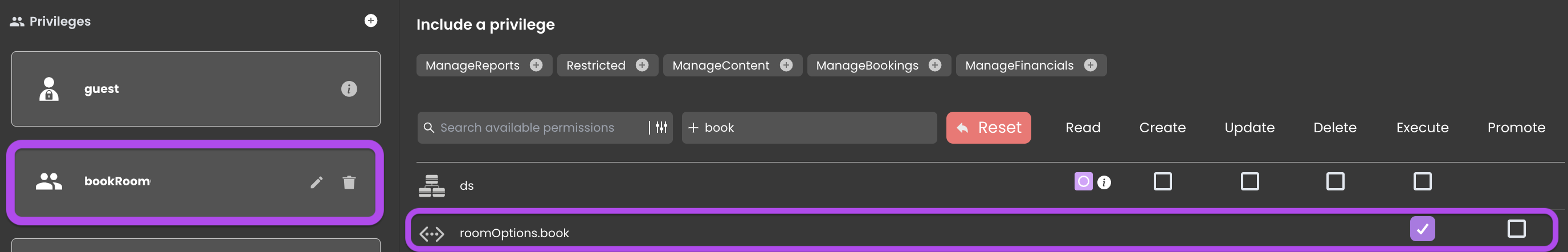
In this context, the bookRoom privilege overrides function permissions set at the DataStore level (Restricted).
Full Access to Gradual Restriction
If no Execute permission is set at any level, it grants full access to all functions defined throughout the Model. Gradual restriction involves using other privileges to restrict specific function execution, as seen in the Employee DataClass, where the register() function execution is restricted to specific privileges.
Promote Permission Use Case
Scenario Overview
In a travel agency's system, dynamic pricing analysis recalculates travel package prices based on demand, seasonal trends, and competitor pricing. Key roles include:
-
The
Sales Managerrole fully controls Read access to thePricingDataclass, including the execution of its functions (Dataclass functions, entity functions, and entity selection functions), such as theanalyzePricingfunction, to ensure confidentiality. -
Although the
Agentrole is restricted from accessing thePricingDataclass, there are specific scenarios where theAgentmay need to utilize theanalyzePricingfunction to conduct a pricing analysis in response to special requests.
Promote Permission Configuration
If an Agent receives a special request, they need Execute permission for the analyzePricing function to generate a customized pricing quote. This allows users with the Agent role to directly execute the function.
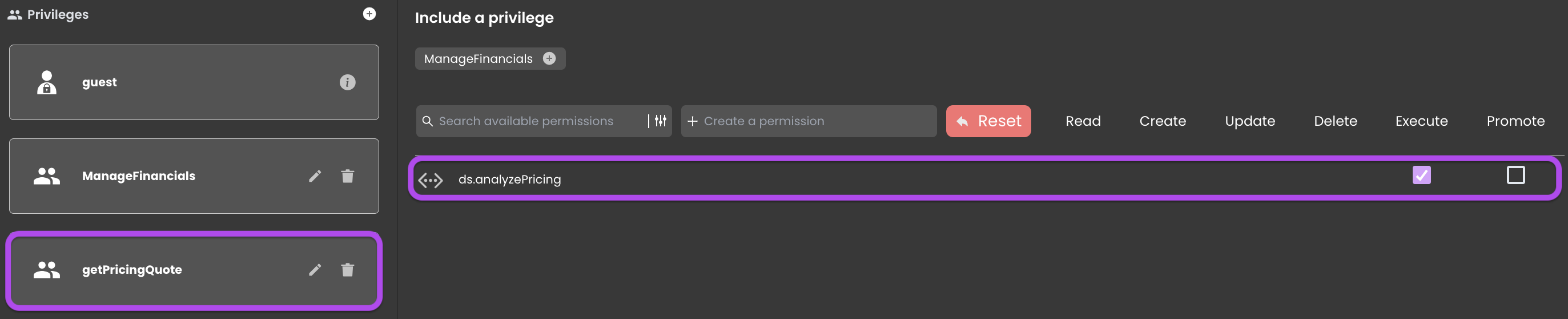
However, due to restricted access to the Pricing Dataclass limited to the Sales Manager role:
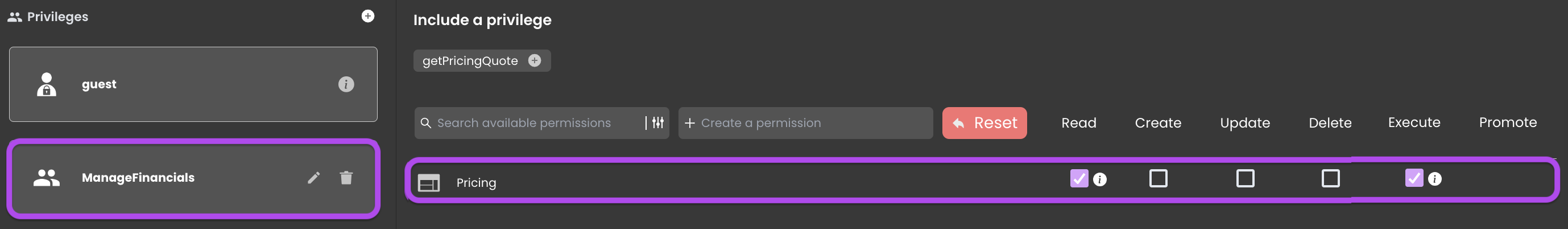
Executing the function code attempting to Read data from it would result in a No permission to read for the Pricing dataclass error.
Therefore, It becomes essential to include Promote permission for the analyzePricing function within the ManageFinancials privilege:
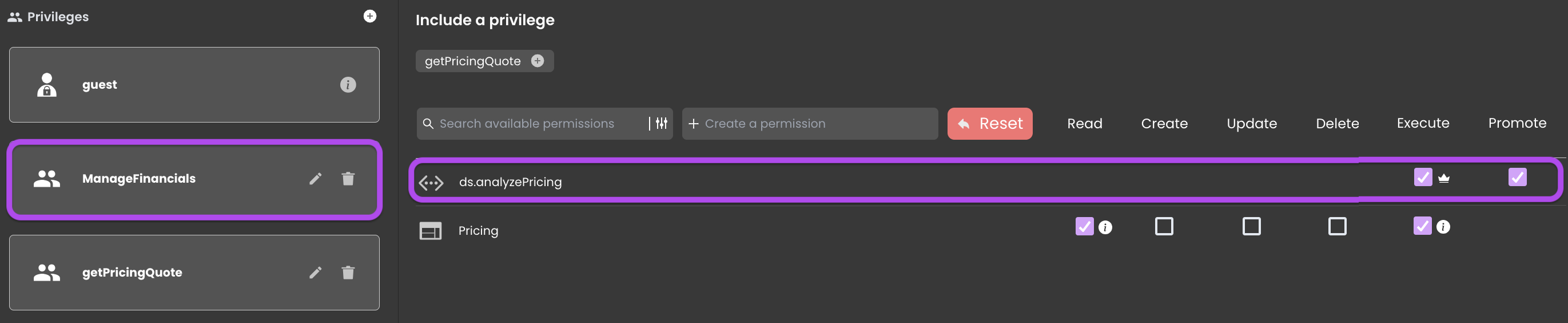
The icon indicates that the function has been promoted by another privilege. Hover over the privilege name, and clicking on it will direct you to the privilege promoting the function.

This configuration explicitly specifies that when the analyzePricing function is executed within a session holding the Agent role, which lacks permission for the Pricing resource, it temporarily integrates the ManageFinancials privilege into that session during function execution. This temporary elevation allows the function to be executed without granting permanent access.
Add the Execute permission in the privilege associated with the role that needs to directly perform the function. Meanwhile, the Promote permission is configured in the privilege that grants broader control over the resources involved in the function, providing a temporary elevation of privileges during the function's execution.