Attribute Permissions
Purpose and Scope
Attribute permissions enable you to control access to specific attributes within dataclasses. These permissions dictate what actions users are allowed to perform on individual attributes, providing fine-grained access control over your data.
Configuring Attribute Permissions
Attribute-level permissions can override or supplement those set at the dataclass level. To set attribute permissions for a specific privilege:
- Select the resource name, like the
netProfitMarginin theReportingdataclass, from the dropdown list. - Or, type the resource name directly into the search bar.
The icon in the dropdown list indicates Attribute ressources.
Example: Attribute-Level Access Control
While Dataclass permissions cascade down to attributes, you can adapt them by overriding or supplementing permissions as needed.
For instance, the ManageReports privilege, assigned to users with the Sales Manager role, allows unrestricted access to the Reporting Dataclass.

However, this inadvertently exposes sensitive data, such as netProfitMargin and totalExpenses attributes, to individuals outside the financial department. Consider a scenario where a user with a Sales Manager role attempts an HTTP request to the netProfitMargin attribute REST API endpoint. This unchecked access permits unauthorized viewing of confidential financial data:
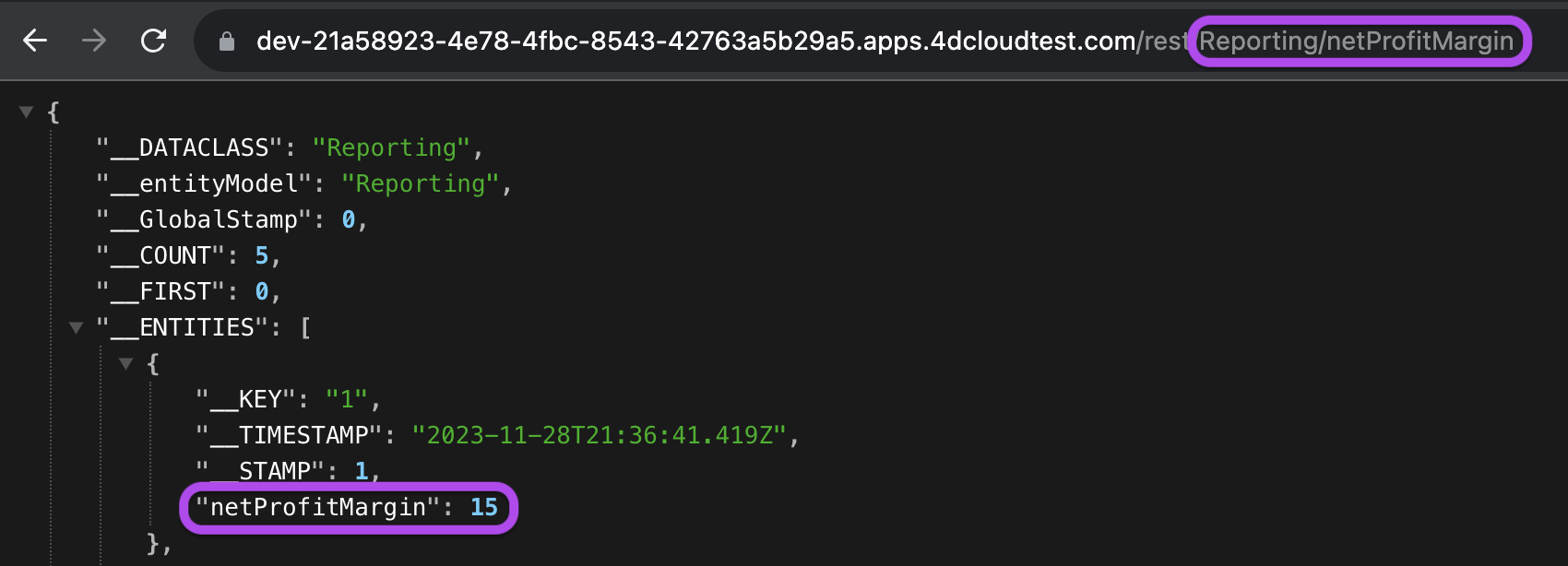
To address this issue, refine the attribute permissions to restrict access to sensitive attributes:

By setting attribute permissions in the ManageFinancials privilege, you allow users with the ManageReports privilege to access the Reporting dataclass while restricting access to confidential attributes like netProfitMargin and totalExpenses.
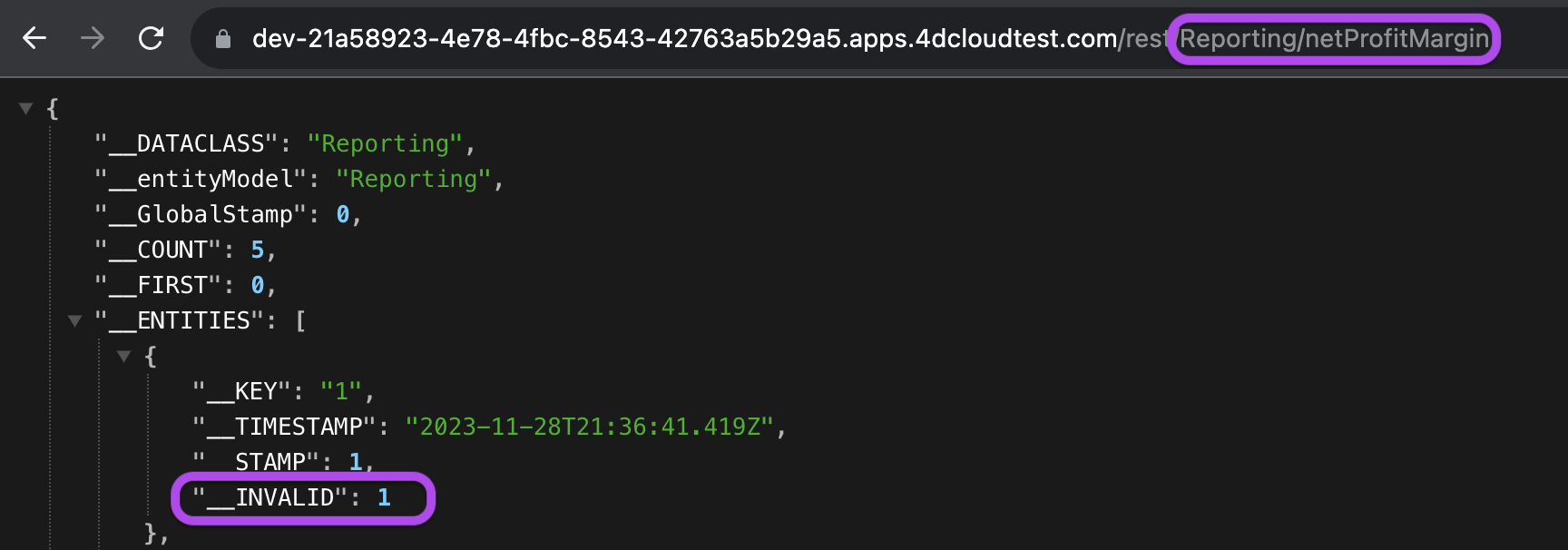
In the response, the presence of __INVALID: 1 indicates that the attribute is marked as invalid, signaling that the user lacks the necessary permissions to access or modify it.