$querypath
Functionality
Definition
The $querypath endpoint allows developers to understand how queries are executed in the backend. It provides a step-by-step breakdown of the query execution, showing each operation, its performance, and the results obtained at each stage. It also reveales optimization techniques and the exact path taken by the server to fetch the required data.
For additional information, please consult the "About queryPlan and queryPath" documentation.
Syntax
To use the $querypath parameter, use the following syntax:
GET /rest/{{dataClass}}/?$querypath=true
Properties Returned
General Properties
The response from the $querypath endpoint is structured to provide a detailed insight into the query execution process:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
__queryPath | Object | Contains the detailed steps taken to execute the query. |
__extendedQueryPath | Object | Provides an advanced, detailed logical structure of the query execution. |
__DATACLASS | String | The data class targeted by the query. |
__entityModel | String | The entity model used during the query. |
__GlobalStamp | Integer | Global modification timestamp indicating the last update across the server. |
__COUNT | Integer | Number of entities returned by the query. |
__FIRST | Integer | Index of the first returned entity. |
__ENTITIES | Array | Detailed information about the entities affected by the query. |
__queryPath Details
Detailed information about the steps involved in the query:
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
steps | Array | An array containing detailed steps of the query execution process. |
Within steps Array
Each step within the query execution path is detailed:
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
description | String | Describes the action taken, e.g., a join or filter operation. |
time | Number | Time in milliseconds taken to execute this part of the query. |
recordsfounds | Number | Number of records found as a result of this step. |
steps | Array | Nested steps detailing sub-operations or subsequent actions in the query path. |
__extendedQueryPlan Details
Provides a more intricate view of the query execution strategy:
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
type | String | Type of node in the query plan, e.g., LogicOperatorNode. |
logicOper | String | Logical operator used, e.g., And. |
parts | Array | Details of operations performed in the query plan. |
Within parts Array
Each element in the parts array represents a detailed aspect of the query execution:
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
type | String | Specifies the type of operation, like JoinNode or SeqNode. |
field | String | Field involved in this part of the query. |
table | String | Table that the field belongs to. |
instance | Integer | Instance identifier for complex queries involving multiple uses of the same table. |
oper | String | Operator used in the query, such as > or ===. |
value | Various | The value used in the operation, reflecting the filter or condition applied. |
timeTaken | Number | Execution time for this part of the query. |
foundRecords | Number | Number of records that matched this part of the query. |
__ENTITIES Details
Information about the entities affected by the query:
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
__KEY | String | Unique key for the entity. |
__TIMESTAMP | String | Timestamp of the last update to the entity. |
__STAMP | Integer | Version stamp for the entity. |
ID | Integer | Identifier of the entity. |
Quantity | Integer | Example attribute, e.g., quantity in an order. |
Purchaser | Object | Example attribute, e.g., details about the purchaser, using deferred loading. |
Combining with Other Parameters
The $querypath parameter can be combined with other parameters to trace the execution path of a query, providing insights into the query's performance and optimization opportunities:
-
$filter: Apply filters to the dataset and trace the path to see how they affect the query execution.
-
$orderby: Observe how sorting impacts the execution path.
-
$top/$limit and $skip: Check the effect of limiting and skipping records on the query execution path.
-
$expand: Include related data and trace how joining related tables or collections influences the execution path.
-
$attributes: Specify which attributes are included in the query and understand their impact on the execution path.
-
$method: Combine with various method operations to analyze their execution paths.
-
$compute: Evaluate the impact of computations on the query execution path.
-
$entityset: Analyze the execution path for operations involving entity sets.
-
$savedfilter: Save and reuse filters to analyze their impact on the query execution path.
-
$savedorderby: Save and reuse sorting criteria to analyze their impact on the query execution path.
Sample Usage in Postman
How to Use:
- Method: GET
- URL:
/rest/Orders?$filter="Quantity > 4 AND Purchaser.Name = user2"&$querypath=true
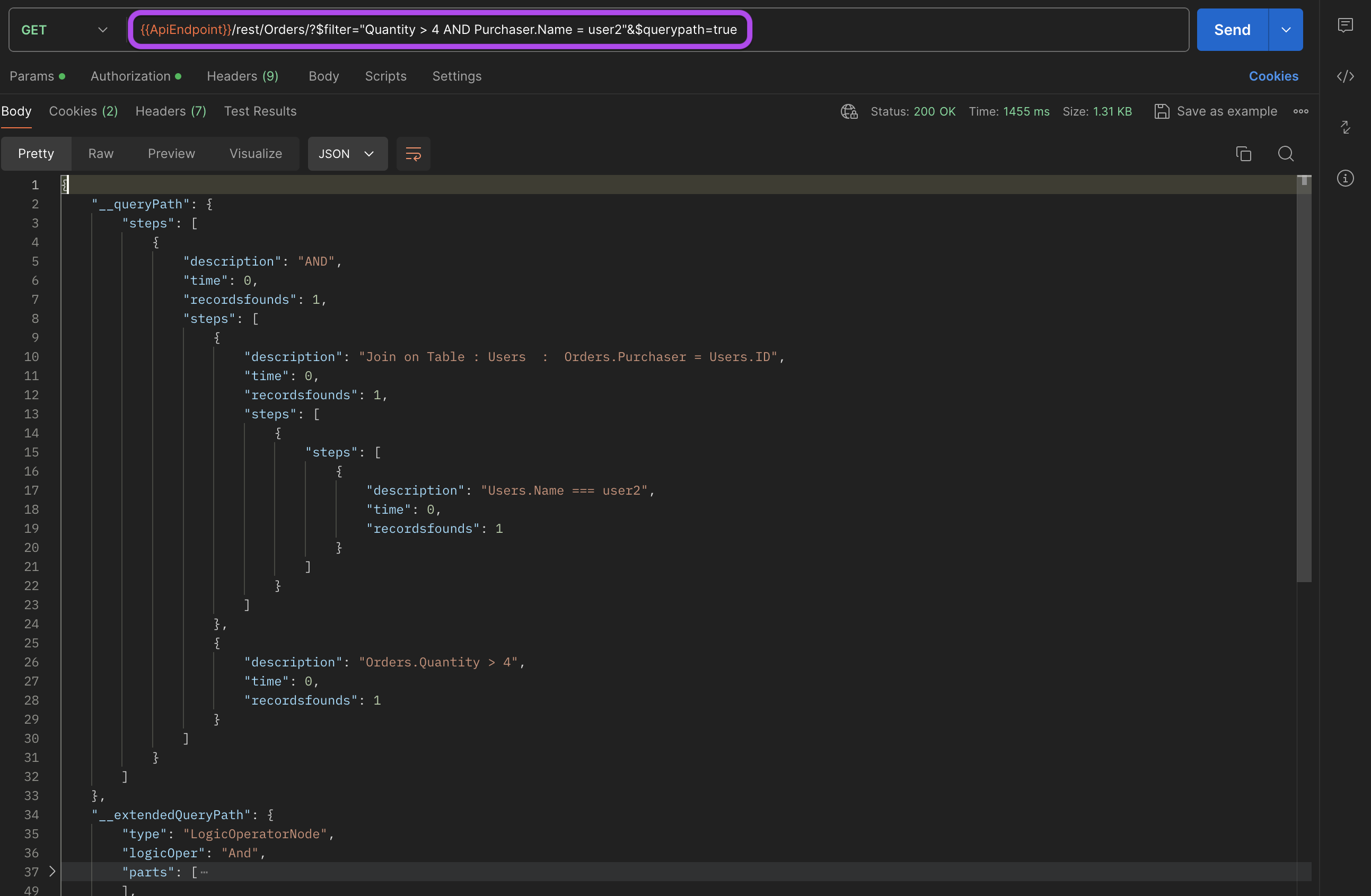
Sample Response
The response structure for the $querypath endpoint looks something like this in practice:
{
"__queryPath": {
"steps": [
{
"description": "AND",
"time": 0,
"recordsfounds": 1,
"steps": [
{
"description": "Join on Table : Users : Orders.Purchaser = Users.ID",
"time": 0,
"recordsfounds": 1,
"steps": [
{
"steps": [
{
"description": "Users.Name === user2",
"time": 0,
"recordsfounds": 1
}
]
}
]
},
{
"description": "Orders.Quantity > 4",
"time": 0,
"recordsfounds": 1
}
]
}
]
},
"__extendedQueryPath": {
"type": "LogicOperatorNode",
"logicOper": "And",
"parts": [
{},
{
"type": "SeqNode",
"field": "Quantity",
"table": "Orders",
"instance": 0,
"oper": " > ",
"value": 4,
"timeTaken": 0,
"foundRecords": 1
}
],
"timeTaken": 0,
"foundRecords": 1
},
"__DATACLASS": "Orders",
"__entityModel": "Orders",
"__GlobalStamp": 0,
"__COUNT": 1,
"__FIRST": 0,
"__ENTITIES": [
{
"__KEY": "20",
"__TIMESTAMP": "2024-05-09T17:01:36.995Z",
"__STAMP": 1,
"ID": 20,
"Quantity": 5,
"Purchaser": {
"__deferred": {
"uri": "/rest/Users[2]",
"__KEY": "2"
}
},
"OrderedProduct": {
"__deferred": {
"uri": "/rest/Products[2]",
"__KEY": "2"
}
},
"paymentsSelection": {
"__deferred": {
"uri": "/rest/Orders[20]/paymentsSelection?$expand=paymentsSelection"
}
}
}
],
"__SENT": 1
}